Weight Loss Treatments
Overweight and obesity result from a complex interaction of genetic, behavioral, and environmental factors. Understanding and addressing these factors becomes important as global rates of these conditions continue to rise. In this guide, we explore the best weight loss treatment options from a purely medical perspective.
Lifestyle Changes
Healthcare professionals begin treating overweight and obesity by recommending lifestyle changes. These adjustments are foundational to any weight loss strategy and involve both dietary modifications and increased physical activity. The goal here is to create a sustainable balance where the calories consumed are fewer than those expended, leading to weight loss.
Weight-Loss Programs
When general lifestyle changes are not enough or specialized guidance is needed, your doctor might refer you to specialists or a dedicated weight management team. These experts are trained to design personalized weight-loss plans that suit your unique health needs and goals.
How Do Weight-Loss Programs Work?
Weight-management programs are divided into two phases: the weight loss phase and the weight maintenance phase. Although physical activity is important for maintaining a healthy weight, dietary restriction influences the rate of weight loss.
Since activity only accounts for about 15 to 30 percent of daily energy expenditure, while food intake represents 100 percent of energy intake, managing dietary calories is essential for effective weight loss.
Dietary programs vary widely, but they all typically involve adjustments to the intake of the three macronutrients: proteins, carbohydrates (CHO), and fats. The specific balance of these nutrients can differ between diets, but the core principle remains: reducing overall energy intake to create a caloric deficit.
Weight-Loss Medicines
Healthcare professionals may prescribe weight-loss medications as an adjunct to dietary and exercise modifications; these medications can also aid in maintaining weight loss once you achieve it, which means that you must adhere to healthy eating plans and stay active while on these medications.
Weight-Loss Medicines Considerations and Cautions
While these medications can effectively aid weight management, they are not without risks and side effects. You should thoroughly discuss these drugs’ benefits and potential drawbacks with your doctor.
Weight-Loss Surgery
Weight-loss surgery, or metabolic and bariatric surgery, is a powerful intervention that aims to help people achieve substantial weight loss by making changes to the digestive system. This type of surgery is typically recommended for people with a body mass index (BMI) of 35 or higher or for those with a lower BMI who have serious health problems related to obesity, such as type 2 diabetes or sleep apnea.
Surgical Options
There are many types of bariatric surgery; below are some of them:
- Gastric Sleeve (Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy)This procedure removes approximately 80% of the stomach, leaving a banana-shaped section sealed with staples. It reduces the stomach’s capacity, leading to earlier satiety.
- Gastric Bypass (Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass)At this procedure, the stomach is divided into a small upper pouch and a much larger lower remnant pouch, and then the small intestine is rearranged to connect to both.
It reduces the amount of food the stomach can hold and alters the body’s ability to absorb calories and nutrients.
- Adjustable Gastric BandThis procedure involves placing an inflatable band around the upper portion of the stomach to create a small stomach pouch above the band with the rest of the stomach below. Your doctor can adjust the opening size from the pouch to the rest of the stomach by filling the band with saline.
- Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal SwitchThis procedure starts with a gastric sleeve surgery followed by a resection of the majority of the intestine. It significantly reduces the absorption of calories and nutrients, leading to more weight loss than other surgeries.
Weight-Loss Surgery Considerations and Risks
While bariatric surgery can be an effective tool for significant weight loss, it comes with risks and requires a commitment to lifestyle changes to be successful. Complications can include nutrient deficiencies, surgical complications, and the need for revision surgeries. Therefore, thorough pre-operative assessment and long-term post-operative care are necessary to ensure the treatment’s safety and effectiveness.
Non-Invasive Weight-Loss Treatments
Non-invasive technologies offer a means to reduce body fat, improve skin appearance, and enhance overall body contours through various mechanisms. Here’s a closer look at some of the most prominent non-invasive treatments available today:
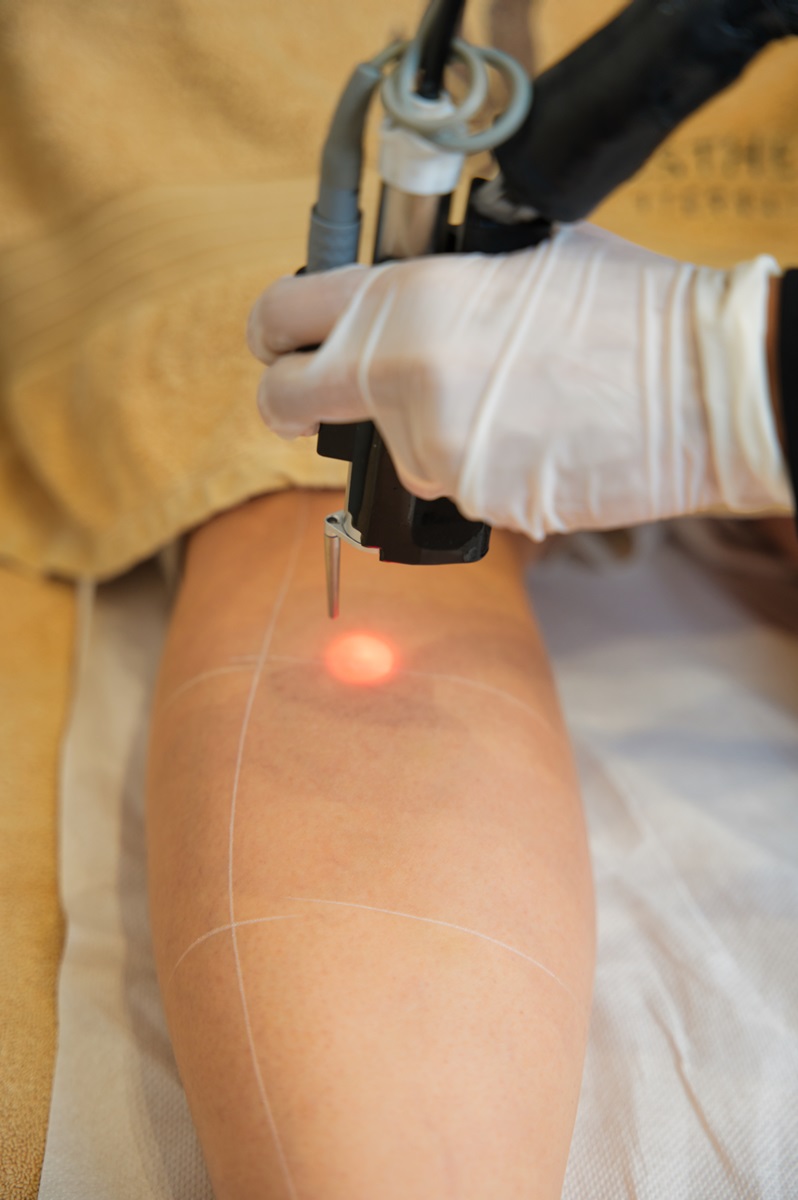
- High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU)Introduced in 1942 for therapeutic applications, HIFU was initially used for treating organ tumors, kidney stones, and uterine fibroids. Over the past decades, the technology has evolved, and its application has expanded to include body contouring through the reduction of adipose tissue. HIFU works by focusing high-energy ultrasound waves on a specific area, creating heat and destroying fat cells without damaging surrounding tissues.
- Radiofrequency (RF)Radiofrequency therapy utilizes electromagnetic waves, which were initially employed to treat periorbital wrinkles, rhytids, and skin laxity. Nowadays, RF is widely used for its effectiveness in body contouring, skin tightening, and cellulite reduction; it increases the temperature of deeper skin layers while sparing the epidermis, effectively inducing skin contraction and promoting fat reduction through thermal energy.
It is worth mentioning Morpheus; which is a Fractional Radiofrequency Microneedling device used to rejuvenate skin and stimulate collagen production in the underlying layers of the dermis. By combining microneedling with radiofrequency energy, Morpheus8 enhances the effectiveness of traditional RF treatments, providing more significant improvements in skin texture, tone, and firmness.
- Cryolipolysis (CoolSculpting)Developed as a body contouring technique in 2007, Cryolipolysis (CoolSculpting or Fat Freezing) stands out due to its unique approach of using cold to reduce fat. Weight loss treatment with coolsculpting method operates on the principle that fat cells are more vulnerable to cold temperatures than other cell types containing more water. By cooling the target area, cryolipolysis causes fat cells to crystallize and die off, a process known as apoptosis (cell death), leading to gradual fat layer reduction.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)Gaining FDA approval in 2010 for fat reduction, LLLT had already been in use for a variety of other medical conditions, including neurologic, ophthalmic, dental, and dermatologic ailments. LLLT works by emitting cold laser energy into the body tissues, which disrupts the stability of fat cell membranes, leading to the release of fat without harming the overlying skin.